Gum Treatments
Gums (known as gingiva) form part of the structure that supports and surrounds the teeth.
Gums along with the jaw bone, holds teeth in position. Gums also protect the jaw bone from bacteria, food and debris. Excellent long term oral hygiene is required to keep gums in good health.
We do regular cleanings (recommended every 6 months) to keep your gums healthy and your teeth clean. The human mouth can develop a variety of gum problems such as gum inflammation, gum infection, gum abscess, recession of gums (and bone), gum pockets and loose gums.
Gum disease is called a silent disease as the early stages are not accompanied by pain. However, as the disease progresses it can lead to vast destruction of gum and bone, resulting in loss of teeth. Treatment for gum conditions can be non-surgical, surgical or laser assisted.
Periodontal Scaling and Root Planing: This non-surgical procedure removes deeper deposits and smoothens the roots of the teeth so that the gum inflammation comes down and gums can reattached back to the tooth.
Flap Surgery: This is a surgical procedure done under local anaesthesia where the gums are opened and deep deposits are completely removed. It is done in areas where Periodontal Scaling and Root Planing is insufficient to remove all the deposits or where additional gum therapies are required.
Recession of gums: If there is sufficient bone support underneath the gums, a gum graft can help to treat receded gums. This may be combined with a small adjustment in the bite to even out biting pressure on the teeth.
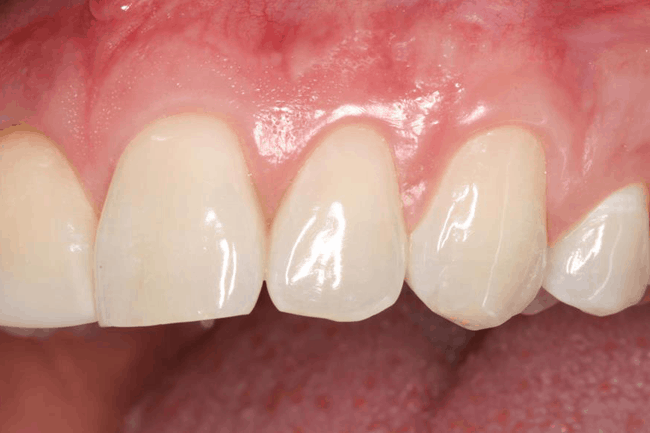
This may be combined with a small adjustment in the bite to even out biting pressure on the teeth. If there is recession of bone, the focus is on maintaining or improving the health of the bone support to the tooth. Depending on the nature of the recession, a bone graft may be placed.
Gum pocket: This is where there is loose gum caused either by gum swelling or bone loss under the gum. The gum forms a pocket (or a flap) where food gets accumulated, causing gum disease, pain and further deterioration of gum and bone. A variety of gum pocket treatment measures are available.
Pigmented (dark) gums: Darkly pigmented gums can be an esthetic concern. This pigmented top layer of the gum can be stripped off exposing lighter gum underneath.
Crown lengthening procedures: Often, front teeth may require minor amounts of gum to be trimmed or shaped so that gums levels/shape are ideal and balanced on both sides of the mouth. In more severe cases, some quantity of gum and bone may need trimming to expose more tooth structure in order to place a crown or to show adequate amount of teeth for cosmetic reasons.
Reducing gummy smile: The reasons for excess gum visibility are many: gums that lie low on the teeth and cover too much teeth surface, tall jaw bone and lips that move high up during smiling or talking. Depending on the cause of the gummy smile, treatment includes trimming away the excess gum and/or re-positioning the upper lip level.